Specification
In the following we provide an exhaustive list of all features supported.
SDN Features
ONOS cluster of all-active N instances affording N-way redundancy and scale, where N = 3 or N = 5
Unified operations interface (GUI/REST/CLI)
Centralized configuration: all configuration is done on the controller instead of each individual switch
Centralized role-based access control (RBAC)
Automatic host (end-point) discovery: attached hosts, access-devices, appliances (PNFs), routers, etc. based on ARP, DHCP, NDP, etc.
Automatic switch, link and topology discovery and maintenance (keepalives, failure recovery)
L2 Features
Various L2 connectivity and tunneling support
VLAN-based bridging
Access, Trunk and Native VLAN support
VLAN cross connect
Forward traffic based on outer VLAN id
Forward traffic based on outer and inner VLAN id (QinQ)
Pseudowire
L2 tunneling across the L3 fabric
Support tunneling based on double tagged and single tagged traffic
Support VLAN translation of outer tag
L3 Features
IP connectivity
IPv4 and IPv6 1 unicast routing (internal use of MPLS Segment Routing)
Subnetting configuration on all non-spine facing leaf ports; no configuration required on any spine port
Equal Cost Multi-Path (ECMP) for traffic across spine switches
IPv6 router advertisement
ARP, NDP, IGMP handling
Number of flows in spines greatly simplified by MPLS Segment Routing
Further reduction of per-leaf flows with route optimization logic
DHCP Relay
DHCP L3 relay
DHCPv4 and DHCPv6
DHCP server either directly attached to fabric leaves, or indirectly connected via upstream router
DHCP client directly either attached to fabric leaves, or indirectly connected via LDRA
Multiple DHCP servers for HA
vRouter
vRouter presents the entire SD-Fabric as a single router (or dual-routers for HA), with disaggregated control/data plane
Uses open-source protocol implementations like Quagga (or FRR)
BGPv4 and BGPv6
Static routes
Route blackholing
ACLs based on port, L2, L3 and L4 headers
Multicast
Centralized multicast tree computation, programming and management
Support both IPv4 and IPv6 multicast
Dual-homed multicast sinks for HA
Multiple multicast sources for HA
API
Provide easy access for 3rd party edge application developers and for the Aether centralized management platform
Support for traffic redirecting, dropping, network slicing and QoS
Data Plane Programmability
Support for Stratum, P4Runtime/gNMI, and P4 programs
Innovative services enabled by programmable data plane:
4G/5G User Plane Function (UPF): GTP encap/decap, usage reporting, downlink buffering and data notifications, QoS and more, with integration with mobile core control plane via PFCP protocol (3GPP standard interface).
Inband Network Telemetry (INT): INT-XD mode with support for flow reports, drop reports, queue congestion reports, with smart filters to reduce volume of reports ingested by the INT collector.
Troubleshooting & Diagnostics
T3: Troubleshooting tool to diagnose broken forwarding paths fabric wide (work in progress)
ONOS-diags: One-click diagnostics collection tool for issue reporting
Topology
SD-Fabric can start at the smallest scale (single leaf) and grow horizontally.
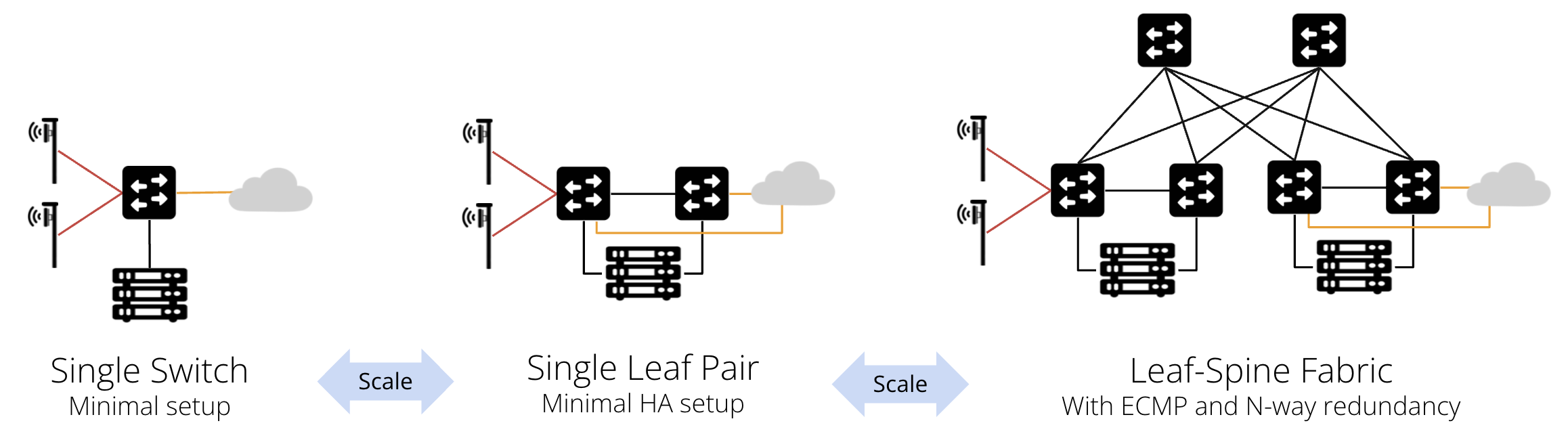
Single Leaf (ToR)
This is the minimum SD-Fabric setup. In this setup, all servers are connected to a single switch.
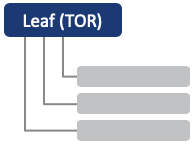
Single Leaf Pair (Dual-Homing)
Compared to a single switch, it provides redundancy in terms of server NIC failure and link failure.
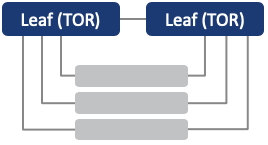
Leaf-Spine (without pairing)
Provide horizontal-scalability for multi-rack deployments, with redundancy for spine switch failures:
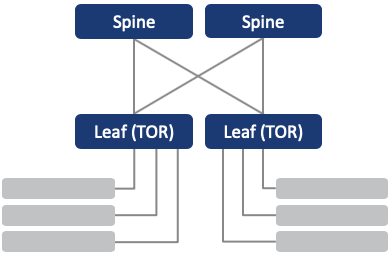
Leaf-Spine (with pairing)
It supports all the redundancy and scalability features mentioned above.
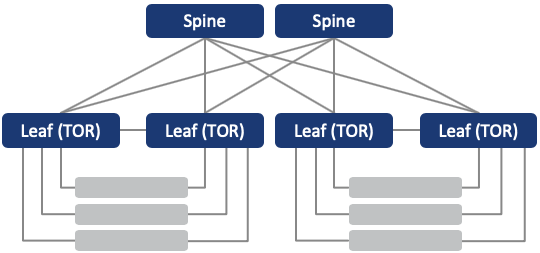
Multi-Stage Leaf-Spine
Multi-stage is specifically designed for telco service providers. The first stage can be installed in the central office, while the second stage can be installed in a field office that is closer to the subscribers. Two stages are typically connected via long distance optical transport.

Resiliency
Provides HA in the following scenarios:
Controller instance failure (requires 3 or 5 node ONOS cluster)
Leaf-spine link failures
Spine switch failure
Further HA support in following failure scenarios with dual-homing enabled:
Leaf switch failure
Upstream router failure
Host NIC failure
Scalability
- In Production
Up to 80k routes (with route optimization)
170k Flows
600 direct-attached hosts
8 leaf switches
2 spine switches
- In Pre-Production
Up to 120k routes (with route optimization)
250k flows
600 direct-attached hosts
8 leaf switches
2 spine switches
- 4G/5G specific
5000 active UEs, 10 calls per second
Security
TLS-secured gRPC connection between controllers and switches (work-in-progress)
Aether-ready
Fully integrated with Aether (5G/4G private enterprise edge cloud solution) including deployment automation, CI/CD, logging, monitoring, and alerting.
Overlay Support
Can be used/integrated with 3rd party overlay networks (e.g., OpenStack Neutron, Kubernetes CNI).
Orchestrator Support
Can be integrated with an external orchestrator, optionally running from the public cloud Supports logging, telemetry, monitoring and alarm services via REST APIs and Elastic/Fluentbit/Kibana, Prometheus/Grafana
Controller Server Specs
Recommendation (per ONOS instance) based on 50K routes
CPU: 32 Cores
RAM: 128GB RAM. 64GB dedicated to ONOS JVM heap
Recommendation (per ONOS instance) for 5K UEs when enabling UPF:
CPU: 1 Cores
RAM: 4GB RAM
White Box Switch Hardware
Multi-vendor: APS Networks™, Dell™, Delta Networks™, Edgecore Networks™, Inventec™, Netburg™, QCT™
Multi-chipset: - Intel Tofino (supports all features, including UPF & INT) - Broadcom Tomahawk®, Tomahawk+®, Trident2 (traditional fabric features only)
1/10G, 25G, 40G, and 100G ports
Refer to Supported Devices list in https://github.com/stratum/stratum for the most up-to-date hardware list
White Box Switch Software
Open source ONL, ONIE, Docker, Kubernetes
Stratum available from ONF
Footnotes
- 1
IPv6 support on the data plane (P4 program) is still work-in-progress.